What is AutoCAD and how can it be used?
An overview of AutoCAD for engineering and architecture
AutoCAD, along with other programs from his own company, Autodesk, have become the unchallenged standard for architecture and engineering, even if it may not have been the original computer-aided design tool.
THE ARCHITECTURE AND ENGINEERING REFERENCE SOFTWARE
AutoCAD is a form of CAD software focused on drawing and modeling in 2D and 3D, if we had to sum it up in a few words. It enables the development of all kinds of buildings and things by enabling the creation and alteration of geometric models with practically endless potential.
Because of its versatility, AutoCAD has expanded beyond its typical use in the domains of engineering and architecture to include graphic and interior design.
Currently, AutoCAD offers a wide range of specialized auxiliary tools that cover all industrial 2D design and 3D modeling sectors.
Autodesk, the first steps

The first version of AutoCAD, the application that John Walker and his team of programmers had previously built, was created in 1982. Michael Riddle was a part of that team.
The popularity of AutoCAD helped the company expand gradually till the current day at a time when computers and software were still in their infancy.
In those years, John Walker left Autodesk and Carol Bartz joined on board. Carol Bartz helped the business multiply its success and AutoCAD’s market penetration became undeniable.
Nowadays, a variety of software tools geared toward design, modeling, rendering, and applications are available from Autodesk.
AutoCAD today
Currently, AutoCAD is refining its features for 2D and 3D design, its interaction with the cloud and its compatibility with other programs, expanding its functionalities.
As, for example:
2D Design
In the latest version, AutoCAD has substantially improved the functions for 2D design, refining the accuracy of the tools by improving some options
- Create dimensions automatically
- Linkable forms with spreadsheets applications
- Storing custom views
- Dynamic blocks
- Ability to extract data from objects, blocks and attributes
- Matrices creation
3D Design
For 3D modeling, Autodesk has focused on improving rendering and compatibility with other programs which complement AutoCAD
- More realistic 3D modeling
- Attach point cloud files
- Apply realistic lighting in renderings
- Create cross-sectional drawings
- Rendering directly in the cloud
Latest features
Following closely on the latest technologies, Autodesk is focusing its efforts on cross-device compatibility and working increasingly in the cloud
- Cloud storage and querying
- Multi-device support
- Quick measurement section
- File’s progress history
- Block pallet
- Improved performance
- Innovative AutoCAD features
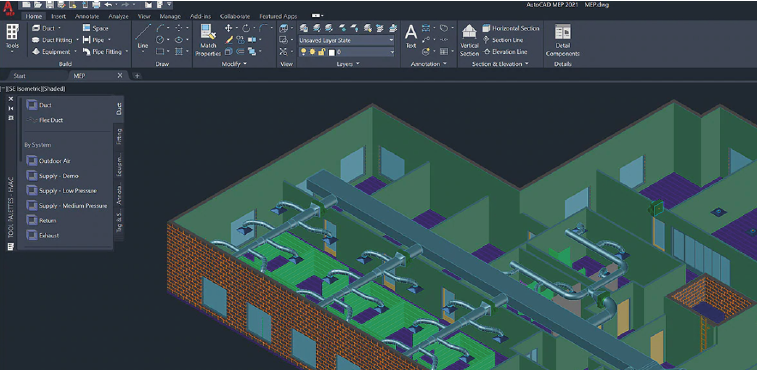
How AutoCAD works
AutoCAD works in layers with vector images, although bitmap images can also be imported, which makes us think directly of Photoshop or Illustrator style programs.
However, its entire interface is designed for the design of plans and structures, and is divided as follows:
- Graphic Area: where we will make our designs
- Options Ribbon: where we will locate the most common actions in our work environment
- Pull-down menu bar and toolboxes
- Status bar, in which we find information about coordinates, grid control buttons or orthometric mode, among others, in vector form.
- Command line, used to interact with the program by commands to get calculations or information that we may need and that AutoCAD automatically collects
Files type
DWG, an AutoCAD native file type, holds all the details regarding the drawings, geometry, and photographs of the original file.
A mechanism of data exchange known as DXF has been developed as a result of the software’s widespread use to view and even open native AutoCAD files (Drawing eXchange File).

Compatibilities with other programs
AutoCAD allows you to export, through its vectorial system, to other graphic design-specific software like Adobe Illustrator or Corel Draw in addition to its standard DWG format.
The same is true for working concurrently with other CAD-type programs.

Blocks and libraries
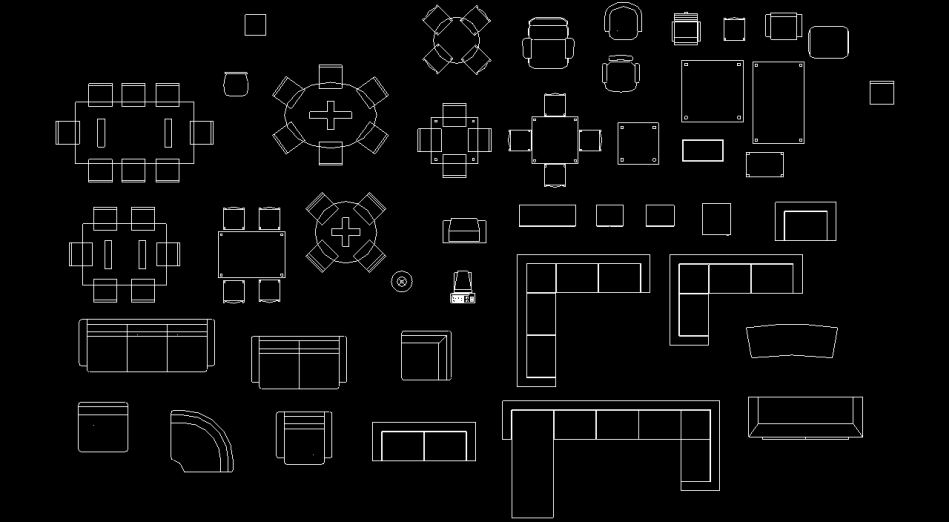
A block in AutoCAD is a building element that can be inserted into a design from a library.
They can represent various types of furniture as well as more complex structures such as slabs, stairs, woodwork, and so on. When including in the design objects that are constantly repeated or of which a large number is required, it is common to use blocks to save time (for example, in the design of the floor plan of a house, the doors and windows).
In general, AutoCAD blocks are organized into themed libraries with various types of specific object blocks, such as the ones we’ve been discussing.
Commands
The commands, which bar can be located in various areas of the screen, from docked to floating, are one way to speed up your work while using AutoCAD.
Commands are instructions that allow you to perform operations quickly, such as saving your work, rounding the edges of an object, inserting items, or creating arcs. The available commands are numerous and easily accessible via the internet.
Some of the most useful are:
- AREA: to calculate the area and perimeter of the object you choose.
- CHSPACE: with this command you can enter the objects in the model from the workspace, scaling them automatically.
- MULTIPLE: replicate the same action until you decide to cancel the command.
- OOPS: restores the last elements you have deleted.
- EXTEND: it serves to lengthen an object until it meets the edges of another one.
AUTOCAD REQUIREMENTS AND LICENSES
AutoCAD is a demanding program that requires a powerful computer powerful to develop its full potential or even be used.
The software is available for both Windows and Mac computers.
Requirements
For the 2020, 2021 & 2023 version, the requirements are as follows:
WINDOWS:
| Microsoft® Windows® 7 SP1 with Update (64-bit only) Microsoft Windows 8.1 with Update (64-bit only) Microsoft Windows 10 (64-bit only) (version 1803 or higher) | |
| Processor | 2.5–2.9 GHz processor |
| RAM | Basic: 8GB Recommended: 16GB |
| Display Resolution | 1920 x 1080 with True Color for conventional displays – High Resolution & 4K Displays |
| Display Card | Basic: 1 GB GPU with 29 GB/s Bandwidth and DirectX 11 compliant Recommended: 4 GB GPU with 106 GB/s Bandwidth and DirectX 11 compliant |
| Disk Space | 6,0GB |
MAC:
| Apple® macOS® Catalina v10.15 (requires Update 2020.1) Apple® macOS® Mojave v10.14 Apple® macOS® High Sierra v10.13 | |
| Model | Apple Mac Pro® 4,1 or later; MacBook Pro® 5,1 or later; iMac® 8.1 or later; Mac mini® 3.1 or later; MacBook Air® 2.1 or later; MacBook® 5.1 or later |
| CPU Type | 64-bit Intel CPU (Intel Core Duo CPU, 2 GHz or faster recommended) |
| RAM | 4 GB of RAM (8 GB or above recommended) |
| Display Resolution | 1280 x 800 display with true color (2880 x 1800 with Retina Display recommended) |
| Disk Space | 3 GB free disk space for download and installation |
Licensing
Another important point to consider is licensing.
Like many other programs, in an increasingly common trend, AutoCAD works with an annual license system to allow its use
AutoCAD for professionals
The AutoCAD professional licenses are available on a monthly, annual or six-yearly basis.
One subscription makes it possible to install AutoCAD on three different computers, with the exception that it can only be used by one user at a time.
A common form of use is with one subscription installed on multiple computers where those who are not the primary user purchase additional standalone licenses.
Similarly, a subscription allows the software to be installed on both Windows and Mac computers.















Leave a Reply